Dizziness is a common complaint that describes various sensations, including feeling like you are spinning, faint, unsteady, lightheaded, floating, weak, or disoriented. It is especially prevalent among older adults, with approximately 30% of the elderly population affected—more commonly in women (36%) than men (22%). Dizziness is often linked to increased fall risk, fear, anxiety, and decreased independence.
What Can Cause Dizziness?
-
Inner ear disorders such as Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo (BPPV)
-
Trauma or injury to the inner ear
-
Damage to the vestibular cochlear nerve, which is responsible for hearing and balance
-
Low blood sugar, low iron levels, or low blood pressure
-
Side effects from medications
-
Medical conditions like diabetes, multiple sclerosis, concussion history, autoimmune disorders, or ear infections
-
Neurological disorders such as Parkinson’s Disease or Stroke
-
Musculoskeletal issues like trauma to the neck, poor posture, muscle strain, arthritis, or inflammation
How Physical Therapy Helps with Dizziness
A physical therapist will evaluate the cause of your dizziness and assess your balance, especially if you are at risk of falling.
1. Education
Physical therapists will explain the likely cause of your symptoms and provide strategies to reduce your fall risk and manage dizziness effectively. They’ll develop a personalized care plan just for you.
2. Home Exercise Program
Based on your assessment, your therapist will create a tailored home exercise plan to:
-
Reduce dizziness symptoms
-
Improve inner ear and vestibular function
-
Enhance balance
-
Strengthen your overall health and well-being
3. In-Clinic Treatment for Dizziness
Treatment typically includes eye, head, and balance exercises designed to:
-
Decrease dizziness
-
Improve walking stability
-
Enhance daily function
All exercises are customized based on your specific needs and comprehensive evaluation results.
Home Exercises for Dizziness Relief
Brandt-Daroff Exercise
Used for: Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo (BPPV), caused by shifting calcium crystals in the inner ear.

How to perform:
-
Begin in an upright seated position.
-
Shift to a lying position on one side, with your nose pointed upward at a 45-degree angle.
-
Remain in this position for 30 seconds to 1 minute, or until dizziness subsides.
-
Return to the seated position.
-
Repeat on the opposite side.
Repetitions: Perform 5 reps on each side, twice daily, as tolerated.
Note: This exercise may provoke dizziness. If symptoms worsen significantly or you feel unsafe, stop and consult a healthcare professional. It’s best performed with someone nearby for safety.
VOR (Vestibular Ocular Reflex) Exercises
Purpose: The VOR helps stabilize your gaze during head movement. Weakness in this reflex can lead to dizziness and poor balance. These exercises help retrain and strengthen the reflex.
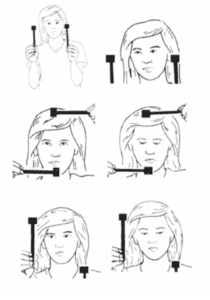
Smooth Pursuit
-
Hold a target (e.g., finger or pen).
Keep your eyes fixed on it while slowly moving it up/down, side to side, and diagonally.
-
Follow the target with your eyes, not your head.
Saccades
-
Hold two stationary objects (like pens), one in each hand, several inches apart.
-
Shift your gaze quickly between the two targets while keeping your head still.
Gaze Stabilization
-
Sit and focus on a stationary object.

-
Move your head side to side, up/down, and diagonally while keeping your eyes on the object.Perform each direction for 30 seconds to 2 minutes, 3–4 times daily.
-
Stop if your dizziness increases more than 3 points on a 10-point scale. Resume once symptoms return to baseline.
Progression Tip: Start in a seated position with a plain background, then progress to standing or walking, using busy backgrounds for added challenge.
Final Thoughts: Why Physical Therapy is Effective for Dizziness
Physical therapy plays a critical role in:
-
Reducing the severity of dizziness
-
Improving vestibular function
-
Enhancing balance and stability
Therapists use targeted strategies such as:
-
BPPV positional maneuvers
-
VOR and gaze stabilization exercises
-
Balance training
-
Patient education
-
Personalized care plans
With a thorough evaluation and individualized treatment, physical therapy can significantly improve quality of life for those suffering from dizziness.
References
-
De Hertogh, W. et al. (2022). Annals of Medicine. Study on dizzy patients in physiotherapy practice
-
Kundakci, B. et al. (2018). F1000Research. Vestibular rehab for chronic dizziness
-
Hall, C. D. et al. (2022). Journal of Neurologic Physical Therapy. Treating dizziness from vestibular disorders
-
Seidenburg, M. (2024). BenchMark Physical Therapy. Exercises for Vertigo and Dizziness






